DCGI approves Hyd-based Dr. Reddy's anti-COVID drug for emergency use
By Newsmeter Network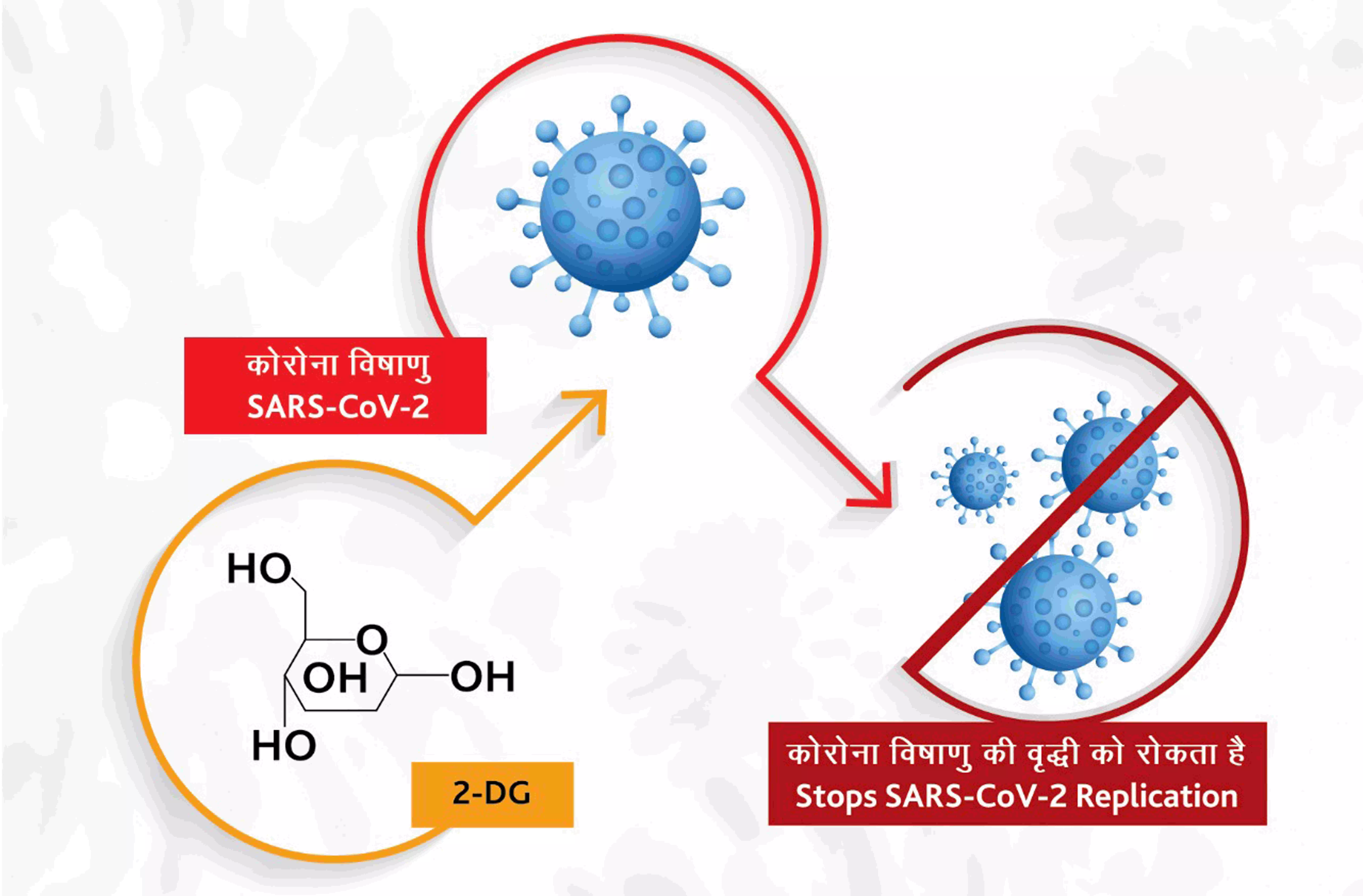
Hyderabad: An anti-COVID drug developed by DRDO in collaboration with Hyderabad's Dr. Reddy's Laboratories has been granted permission for emergency use by the Drugs Controller General of India.
The drug comes in a powder form which is taken orally by dissolving it in water. It accumulates in the virus-infected cells and prevents virus growth by stopping viral synthesis and energy production. Its selective accumulation in virally infected cells makes this drug unique. Being a generic molecule and analogue of glucose, it can be easily produced and made available in plenty in the country.
The anti-COVID therapeutic application of the drug 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) was developed by the Institute of Nuclear Medicine and Allied Sciences (INMAS), a lab of DRDO, in collaboration with Dr Reddy's Laboratories, Hyderabad.
Clinical trial results have shown that 2-DG helps in faster recovery of hospitalized patients and reduces supplemental oxygen dependence. Higher proportion of patients treated with 2-DG showed RT-PCR negative conversion in COVID patients.
In April 2020, during the first wave of pandemic INMAS-DRDO scientists conducted laboratory experiments with the help of Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB), Hyderabad, and found that 2-DG works effectively against SARS-CoV-2 virus and inhibits the viral growth. Based on these results, DCGI's Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) permitted phase II clinical trial of 2-DG in COVID-19 patients in May 2020.
DRDO and Dr. Reddy's Laboratories started the clinical trials to test the safety and efficacy of the drug in COVID-19 patients. Phase II trials, conducted between May and October 2020, found the drug was safe in COVID-19 patients and showed significant improvement in their recovery. In efficacy trends, the patients treated with 2-DG showed faster symptomatic cure than Standard of Care (SoC) on various endpoints. A significantly favourable trend (2.5 days difference) was seen in terms of the median time to achieving normalization of specific vital signs parameters when compared to SOC.
Based on successful results, DCGI further permitted the phase III clinical trials in November 2020. The phase III clinical trial was conducted on 220 patients between December 2020 and March 2021 on a large number of patients at 27 COVID hospitals in Delhi, UP, West Bengal, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
It showed that a significantly higher proportion of patients improved symptomatically and became free from supplemental oxygen dependence (42% vs 31%) by day three in comparison to SOC, indicating an early relief from oxygen therapy/dependence.
In the ongoing second wave of the pandemic, a large number of patients are facing severe oxygen dependency and need hospitalization. The drug is expected to save precious lives and also reduce hospital stay of COVID-19 patients and the burden on health infrastructure.