Explained: Obstructive sleep apnea, causes, symptoms
The common symptoms include snoring, gasping for air during sleep, waking up with a dry mouth, morning headaches, excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty paying attention while awake, and irritability.
By Newsmeter Network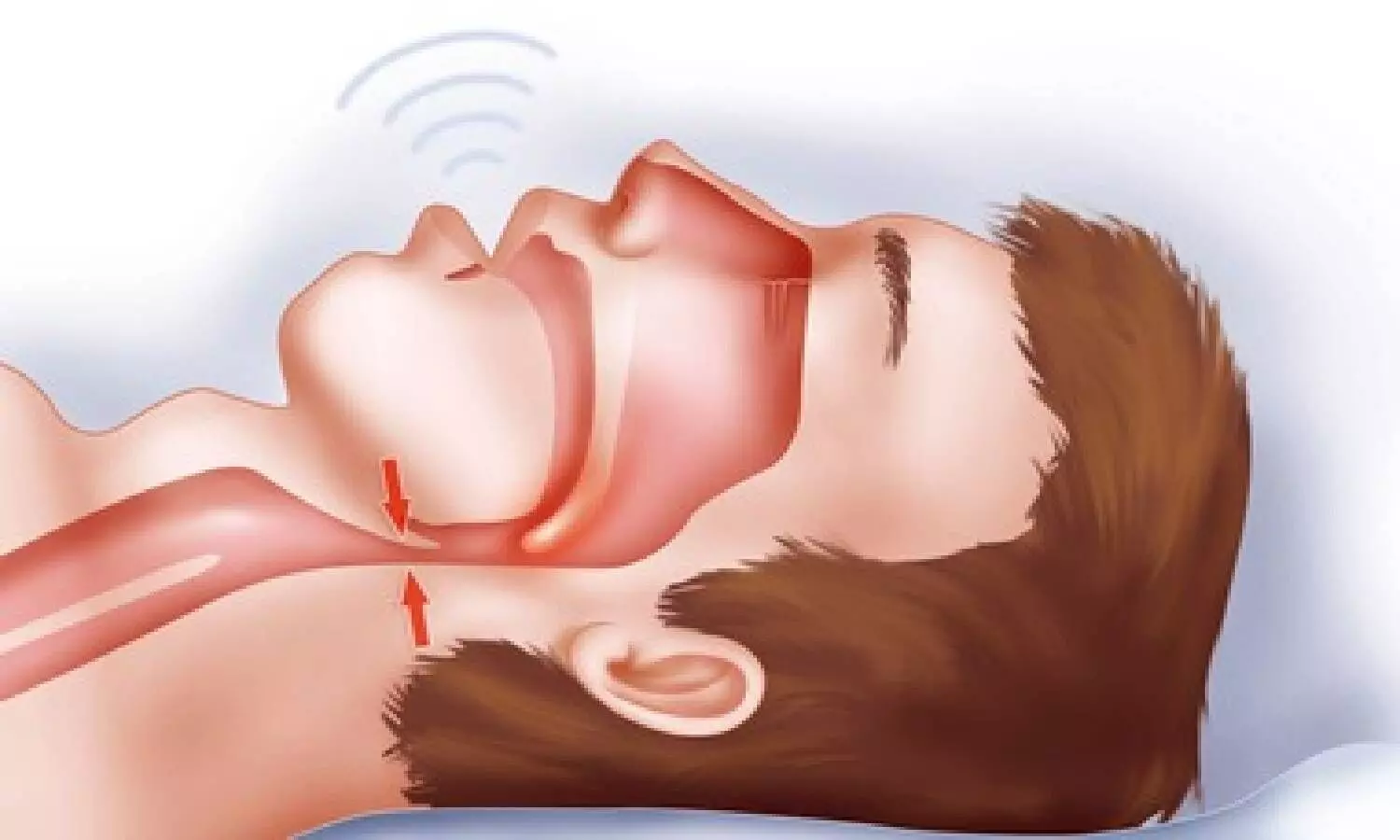
Hyderabad: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a widely prevalent yet under-recognised disorder, is caused by the repetitive collapse of the upper airway during sleep due to the relaxation of the muscles supporting the soft tissues in the throat, such as the tongue and soft palate. The common symptoms include snoring, gasping for air during sleep, waking up with a dry mouth, morning headaches, excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty paying attention while awake, and irritability.
There are certain factors that predispose a person to the development of this form of sleep apnea, including obesity; a narrowed airway (you might have inherited a narrow throat. Tonsils or adenoids also can enlarge and block the airway, particularly in children); genetics also plays a significant role in the development of OSA and many members of the same family can suffer from this disorder; use of alcohol, sedatives or tranquilizers; smoking; and nasal congestion.
Obesity presents a host of disorders and OSA patients due to their weight can have certain associated co-morbidities like congestive heart failure, hypertension, diabetes, Parkinson's disease, and polycystic ovary syndrome. So, patients with any of these associated co-morbidities should always be screened for OSA. In medicine we use a 'STOP BANG' scoring system to screen people for OSA:
S - Do you SNORE while you sleep?
T - Are you TIRED after waking up or for the most part of your day? (This happens because OSA patients have a very unrefreshing sleep)
O - Has anyone OBSERVED you having choking spells while you were asleep?
P - Do you have high blood PRESSURE?
B - Is your BMI (Body Mass Index) more than 35?
A - Is your AGE more than 50 years?
N - Is your NECK circumference more than 40 cms?
G - Is your GENDER male or are you a post-menopausal woman?
If your answer to less than two of the above-listed eight questions is YES, you have a low risk of having OSA. If your answer to three-four questions is YES, you have an intermediate risk of having OSA and if your answer to more than five questions is YES, you have a high risk of having OSA.
Once a person is suspected of having OSA following a screen test, a confirmation is obtained with the help of a Polysomnography (sleep study) where we monitor different parameters of a person's body while they sleep and find out if there is a collapse of the upper airway and what effects it is causing to different organs of the body.
OSA is curable and all it takes is the will to start. Lifestyle modifications, especially weight reduction, go a long way in helping alleviate the OSA symptoms. If the cause of your upper airway obstruction is an anatomical abnormality you may need to undergo a surgical procedure to correct that abnormality. A number of devices are also available that help you augment the patency of your airway and prevent it from collapsing during sleep. But the most effective treatment modality is assisted ventilation in the form of a CPAP or a BiPaP machine. A somnologist helps you choose the best treatment modality for you.
The author is Dr. Abhishek Tandon- MD (Respiratory Medicine), FAGE, DM Resident (Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine) All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur.