Explainer: What is Swab Test for COVID, How does diagnostic test work
By Newsmeter Network
Hyderabad: Thirteen private laboratories found to have discrepancies in the COVID results. The Telangana government informed that one of the private laboratories has reported an extremely high sample positivity rate. The said lab has reported 2,672 positive cases against 3,726 total samples tested. 'The positivity rate is 71.7 % which is a gross variation and discrepancy in the notified positivity rate of COVID-19 to date. The tested negatives are only 962 out of 3,726 samples. The issue needs to be evaluated by an expert committee and until then the data of the said lab has been kept under abeyance", the medical bulletin mentioned.
Scores have been raising doubts over the test used to diagnose COVID-19 patients. Dr Venkateshwar Rao MD (Ophth) AIIMS ,explains the manner in which the test should be conducted and interpreted to avoid discrepancies.
What is the Swab Test for COVID
Nasopharyngeal swabs are the preferred choice for SARS-CoV-2 testing. It involves inserting a long, flexible cotton bud into the nostril and along the nose 'floor'. This is supposed to be done slowly so that it is comfortable.
The swab is rotated several times in order to get enough cells. The sample is then sent to a lab, where it will be tested to determine if the patient’s cells are infected with the virus.
The coronavirus is a RNA virus, which means it uses ribonucleic acid as its genetic material. A process called reverse transcription (RT) is needed to transcribe the RNA into readable DNA.A swab sample doesn't collect much RNA in one go, therefore a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to rapidly make billions of copies so it can be analysed.
The DNA is dyed a fluorescent color, which glows if the coronavirus is present, confirming a diagnosis
How does the diagnostic test work?
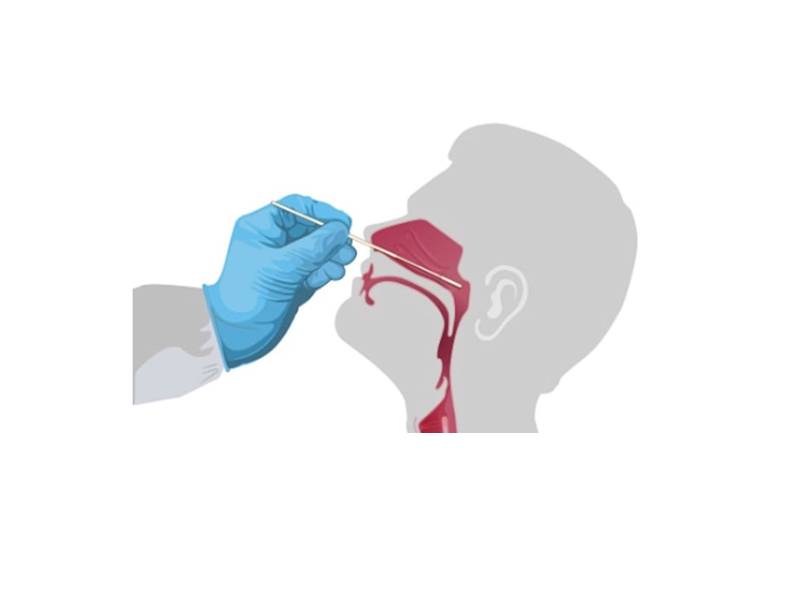
The test most commonly used to diagnose COVID-19 is a molecular test, or PCR test. It works by detecting genetic material from SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. When someone is infected, they have this genetic material in their nose and upper throat. The test uses a sample that is collected with a swab from an area of the nasal passage where viral particles are likely to be present.
Nasopharyngeal swabs are the preferred choice of testing for SARS-CoV-2 worldwide because it collects the most concentrated sample. A long flexible cotton bud is supposed to be inserted deep into the nostril and along the nose 'floor' to collect a mucus sample.
In Home testing kits, people have to take two swabs
- For Nostril
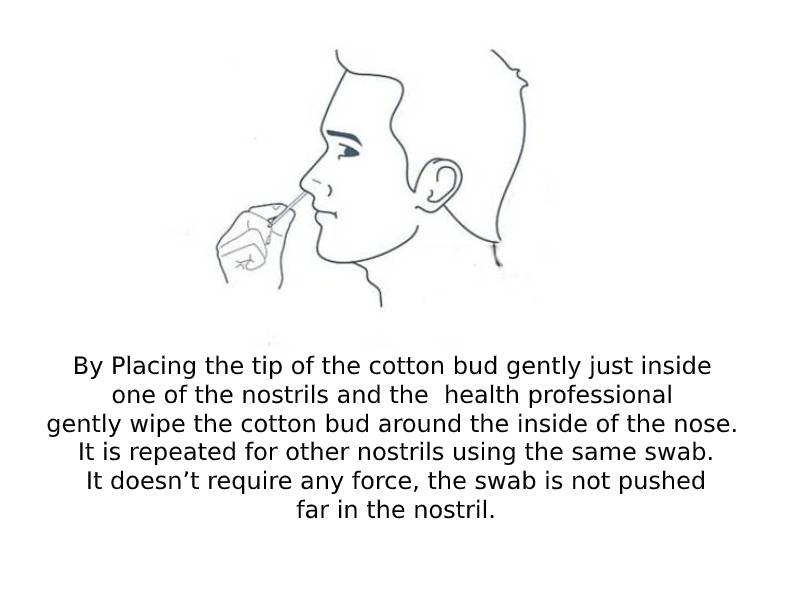
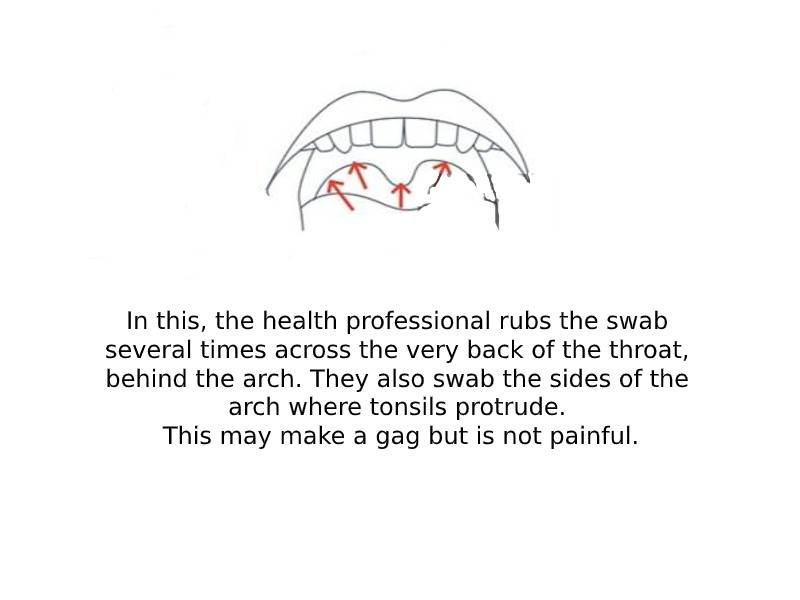
2. For Oropharyngeal
Collecting samples is not easy
Most experts believe that problems with sample collection are the main culprit behind inaccurate testing. False-negative results are likely occurring because health care providers aren’t collecting samples with enough of the virus for the tests to detect.
This can happen because someone doesn’t insert a swab deep enough in the nose or doesn’t collect enough of the sample. False negatives could occur if a person is tested too early or too late during their infection and there isn’t a lot of virus in their cells. And finally, errors can happen if a sample sits too long before being tested, which allows the viral RNA to break down.

Accuracy of Swabs
The accuracy of Viral RNA swabs depends almost entirely on the quality of sampling. Nasopharyngeal(NP) swabs are the preferred choice of testing for SARS-CoV-2 worldwide as it collects the most concentrated sample. Could take 2 samples if it is from the home collection, one from the nostril NP, another oropharyngeal (OP)from the back of the throat from the mouth. The procedure requires a skilled and dedicated health worker. Then there are the inconsistencies in sample collection.
Timing of Testing
The Timing of testing is crucial to minimize false negatives. Test between 5-10thday, ideally on 8th day after exposure to the virus; 3 days after onset of COVID symptoms like fever, cough, loss of smell or taste, and breathing problems. But a still false-negative rate of 20 percent, meaning one in five people who had the virus had a negative test result.
What is a false negative COVID result?
A false negative is a test result that is wrong, because it indicates the person is not infected when they really are. If your test comes negative—have the test done again, or if having symptoms of COVID like fever, cough, loss of smell & taste and breathlessness, then treat as COVID and act accordingly.
What is a false positive COVID result?
A false positive is a test result that is wrong, because it indicates the person is infected when they really are not.
The genetic material from SARS-CoV-2 cannot be confused with the genetic material from other viruses, so the COVID-19 diagnostic test is highly specific. This means it almost never gives a false positive. If you are tested for COVID-19, and the test comes back positive, you can be very sure that you are infected with this virus.

Unfortunately, neither test is equally sensitive. If the specimen collection is not done perfectly, or if you are in an early stage of infection or already partially recovered, your nasal-swab sample might not contain enough viral material to come back positive. There are many stories about patients who tested negative soon after their symptoms began, only to test positive on a test done later.
But a false positive rarely could also come from a lab being contaminated with the virus or with a product from a previous test.